Siri Daily Practice-2
Today I tried to google more about the usage scenario f AI-generated art can keep creating the system map.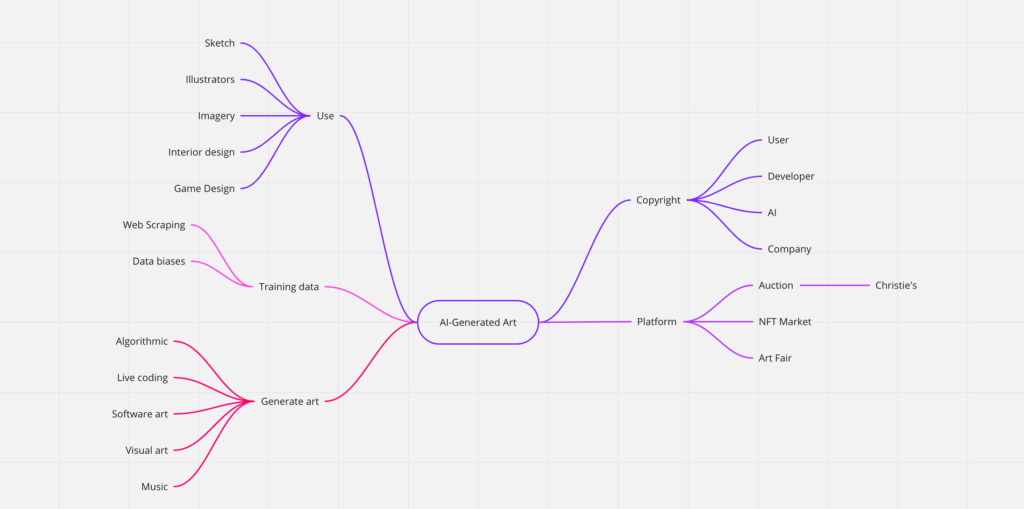
Today I tried to google more about the usage scenario f AI-generated art can keep creating the system map.
Every artist enjoys having the idea that their originality stands out and that their work is completely unique. But if you put in the time and effort, you’ll find that uniqueness is just a romantic idea that doesn’t really exist in the idealized form that people think it does.
Is it stealing, copying, or inspiration if you utilize someone else’s artwork and artificial intelligence to create your own? The largest issue still is: Who owns AI-generated art once it has been produced?
Artificial intelligence (AI) has long produced art. But this year’s technologies, such DALL-E 2, Midjourney, and Stable Diffusion, have allowed even the most inexperienced artists to produce intricate, abstract, or lifelike pieces by merely entering a few words into a text box.
The topic I want to choose is the impact of AI-Generated Art on traditional artists, because of the recent news about An A.I.-Generated Picture Won an Art Prize. and I also noticed that there are more and more digital artists trying to create AI art, which they think is the future trend and similar to the NFT market.
I tied to narrow down my focus using a system map and also used different AI-generated art engines (software) to explore.

Prompt: Digital artists creating AI-generated art and win the prize
By deepdreamgenerator
System Map:
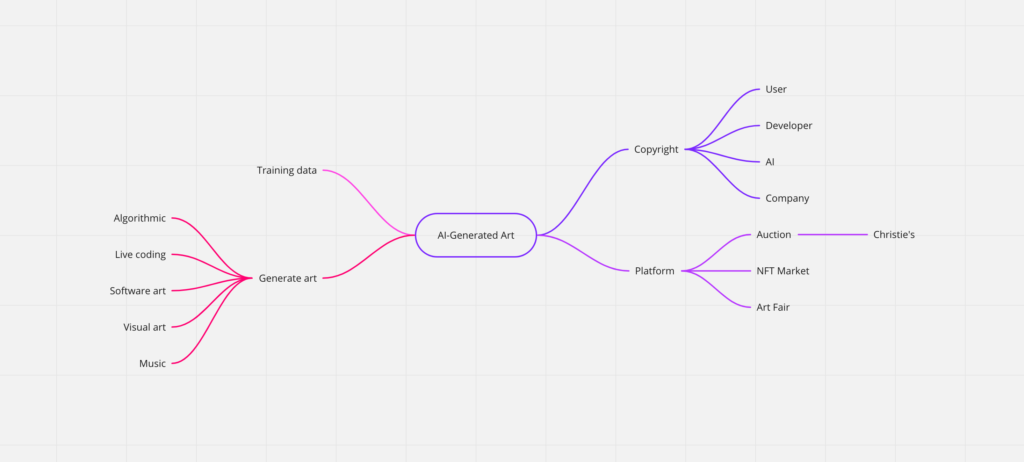
Demo link: https://suirunzhao.github.io/satellitesinspace/#live
Research:
Based on the research and interview, I found that
In order to raise people’s awareness of creating a system of sustainable satellites above us, with long time horizons, I created this guide, with some brief description of the current situation of space.
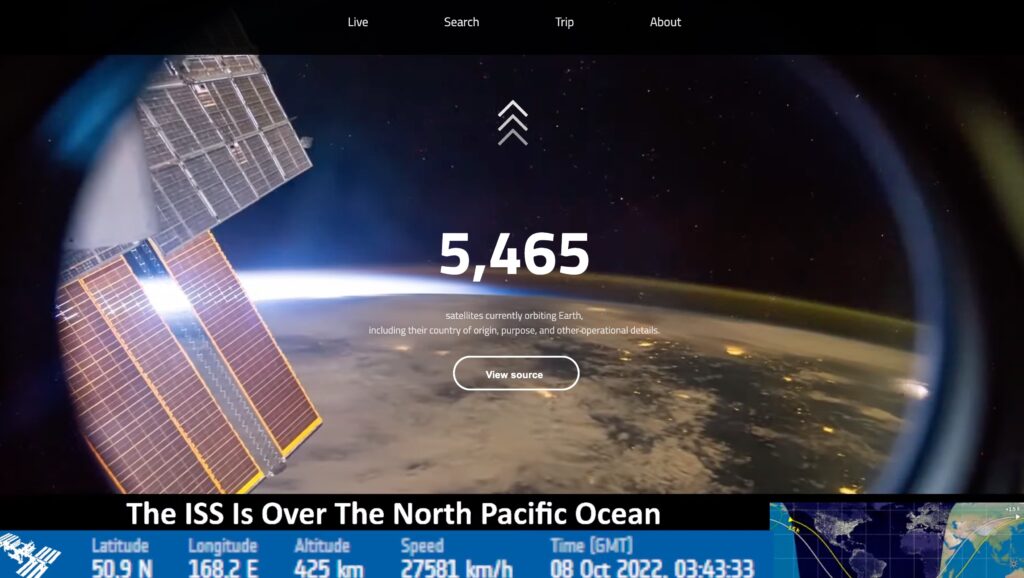
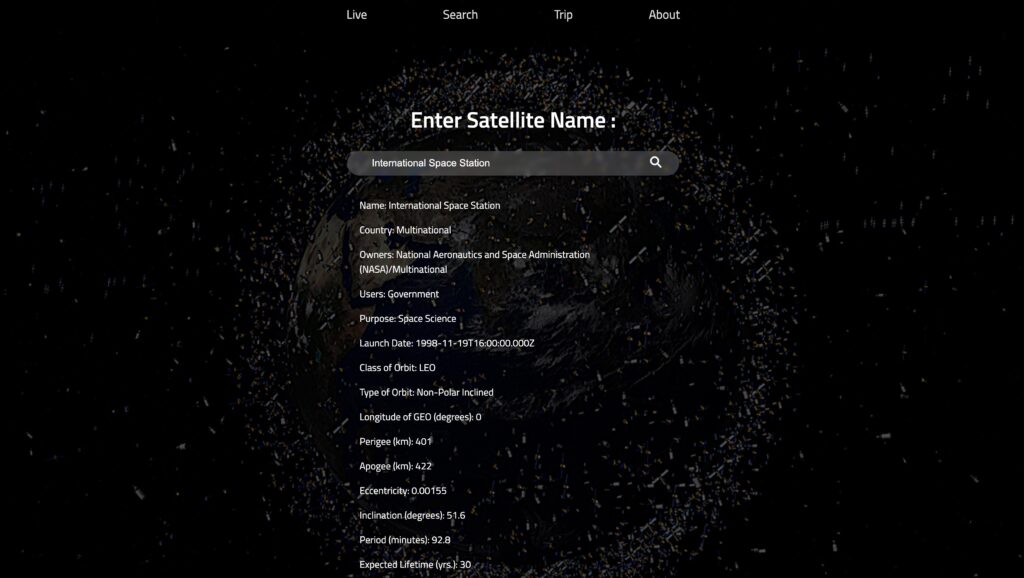
Progress:


References:
Nasa Live Views from the ISS https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=86YLFOog4GM
DEWESoft https://dewesoft.com/daq/every-satellite-orbiting-earth-and-who-owns-them
UCS Satellite Database https://www.ucsusa.org/resources/satellite-database#page-subtitle
Data: https://www.n2yo.com/satellites/
howmanypeopleareinspacerightnow https://www.howmanypeopleareinspacerightnow.com/
Space Guide: https://abraiz01.github.io/Connections-Lab/Week3/Project_1/index.html
Scroll Inspiration: https://neal.fun/deep-sea/
Space Debris and Human Spacecraft: https://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/station/news/orbital_debris.html
SATELLITES FOR SUSTAINABILITY: https://pages.devex.com/satellites-for-sustainability
What’s the environmental impact of space debris and how can we solve it? : https://www.weforum.org/agenda/2022/07/environmental-impact-space-debris-how-to-solve-it/
The current state of space debris: https://www.esa.int/Space_Safety/Space_Debris/The_current_state_of_space_debris
I asked a friend who is fascinated by astronomy, and he is an amateur in space and satellites.
Q: What do you think about the concept of satellite?
A: A satellite is something that orbits, or goes around, a planet or a star, and there are lots of different types. Some natural things are satellites – like the Moon, because it goes around the Earth, but usually, when people talk about satellites they mean the ones that were made by people. They’re sort of like spaceships moving around the Earth, and they’re usually made up of a computer, along with solar panels to get power from the Sun. Sometimes they also have cameras or other scientific tools to help gather information.
Q: What is the situation in space right now?
A: Junkyard…We’ve launched rockets and spacecraft into Earth’s orbit, but now thousands of objects from tiny screws and bolts, to dead satellites encircle the Earth. Transforming the space above us into a junkyard.
Q: What is space junk?
A: any man-made object in orbit around the Earth that no longer serves a useful function
Q: What is the damage of space junk?
A: It directly threatens people in space like ISS(International Space Station), which is in the crosshairs. ISS has already been hit by little bits of debris on a number of occasions and there are no guarantees that other substantial things might not hit it again in the future.
Q: What do you think about the future space environment?
A: Getting worse I guess? You know SpaceX plan to launch 12,000 satellites in space, but we already have 6,000 satellites in space right now and it has already been a junkyard, I think it will become more severe in the future.
According to the interview, I’ve learned lots of space environment problems and also concerned about our future. It’s a good direction to develop my satellite guide.
I’m planning to create a satellite guide website, which has a brief introduction about the number of satellites in space, live stream video from ISS(International Space Station), and the relationship between satellites, orbits and the distance from earth. Users will start from the bottom and scroll up to the top(maybe endless).
The form is typically used for the popularization of science, mainly users might be students and people who have an interest in astronomy
If I tried a different form, I would probably recreate a world map using the satellite states concept, or an Ikea guide for setting up a satellite, or SpaceX infomercial AD.
I think these forms I mentioned above are all well-suited to the metaphor for my satellite topic(need some help)
Draft link: https://suirunzhao.github.io/ConnectionsLab_A3/satellitesinspace/
Inspiration/References:
https://abraiz01.github.io/Connections-Lab/Week3/Project_1/index.html
I totally agree with Lakoff and Johnson about “argument is a war”. The metaphor of “argument is a war” influences how we conceive, understand and act on arguments because it is embedded in our culture and is part of our conceptual system, which has a strong cultural foundation. Metaphors construct concepts in our daily lives, and this construction is reflected in our ordinary literal language. When you use these metaphorical expressions, such as “we have to gamble” or “we have to make theoretical constructions,” people do not think you are using metaphors, but rather saying something ordinary and appropriate to the context. But the way you talk about, think about, and even experience these life situations is indeed constructed by metaphor.
I couldn’t come up with my commonly use the metaphorical system but it reminds me of the differences between the Chinese metaphorical system and the US system. For example, “Dog” is considered a pet in the western countries, with a positive meaning, while in China it is considered derogatory, such as “walk dog”, he is a mad dog “biting everywhere”, etc.; and then, The different concepts of “dragon” in Chinese and English have given rise to the term “Four Little Tigers/Four Litter Dragons(in Chinese)”, which is used to describe four economically developed countries or regions in Asia to show that their economic power is booming. If translated directly as “four little dragons”, it would be an unlucky omen. “Dragon” in the Western conceptual system is a monster that hurts people, while “tiger” is a symbol of good luck and power. Therefore, I believe that metaphorical systems differ greatly in the conceptual systems of different cultural groups.
As for satellites, there are also other metaphors like 1. company, people may use satellites to describe the company of their lovers/families. 2.Satellites countries/states/cities, which is a country that is formally independent in the world, but under heavy political, economic, and military influence or control from another country.
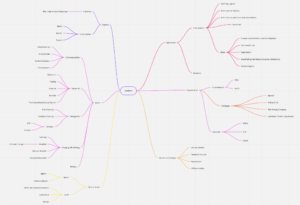
I learned a lot from the concept map and also discovered some new aspects such as space law and the ethics of satellites. Although the smart use of space can enhance life on earth. Satellites are reducing emissions in the aviation industry by optimising flight paths and help container ships boost efficiency and profitability. Elsewhere, space technology helps us measure global carbon emissions more accurately, allows farmers to boost yields and feed the world’s growing population more sustainably. Satellites will be essential if we are to connect people who have yet to use the internet. Whole industries, from mining to retail, simply would not be able to operate without satellite communications. When I explored deeper than last week, I found that 1. the rise in the number of satellites being launched into space is unsustainable. 2. Satellites mega-constellations pose a risk to climate and the environment. 3. Tighter global regulation is needed to ensure space sustainability.
Q1: Which system (type of stakeholder) that Easterbrook identified did you find your own understanding of GMOs most aligned with? Why? What are some of the stakes of these stakeholders?
System 8, A system of sustainable agriculture, with long time horizons, is the system I aligned with my understanding of GMOs. As a student with the food safety background and who graduated from an agricultural university, I have studied specific assessments and safety laws for GM foods. In fact, GM foods are subject to systematic and comprehensive safety evaluation before they are marketed. China has established a safety evaluation technology system that is in line with international standards, which includes nutritional and toxicological evaluations in the area of food safety. Therefore, after the safety evaluation of these products, there is no problem in terms of food safety.
As for sustainable agriculture, we rely on excessive inputs of chemical fertilizers and pesticides to achieve high yields in agriculture at present, which actually puts pressure on the environment, and this problem is becoming more and more prominent.In terms of labor demand, rural laborers are gradually moving to the cities and towns, and this contradiction is becoming increasingly prominent. To solve these problems, we need large-scale, mechanized and intensive cultivation, and GM crops can meet such needs. However, GMOs are helping to solve these problems, although I’m not a 100% supporter I think using GMOs to break through bottlenecks that other biological breeding technology occurred is necessary. We still need to evaluate of the effectiveness, the ability to compete for survival, and the evaluation of biodiversity, including plants, animals, and other aspects.
The stakeholders of system 8 might be farmers, government, enterprises and customers.
Q2: Using your own topic for research, can you Identify 3 stakeholders (groups or phenomenon) with different perspectives, and then describe the system (the stakes) from which they are operating?
Stakeholders of Satellites:
There are two definitions of the satellite:
1. Natural satellite which in the most common usage, an astronomical body that orbits a planet, dwarf planet, or small Solar System body (or sometimes another natural satellite)
2. Artificial satellite is an object intentionally placed into orbit in outer space.
However, the artificial satellite is mostly people referring to the satellite.
Satellites are placed from the surface to orbit by launch vehicles, and then change or maintain the orbit by propulsion. In 2018, about 90% of satellites orbiting Earth are in low Earth orbit or geostationary orbit, a small number of satellites orbit other bodies (such as the Moon, Mars, and the Sun) or many bodies at once (two for a halo orbit, three for a Lissajous orbit).
The first artificial satellite to be launched into the Earth’s orbit was the Soviet Union’s Sputnik 1, on 4 October 1957.
Earth observation satellites gather information for reconnaissance, mapping, monitoring the weather, ocean, forest, etc. Space telescopes take advantage of outer space’s near perfect vacuum to observe objects with the entire electromagnetic spectrum. Because satellites can see a large portion of the Earth at once, communications satellites can relay information to remote places. The signal delay from satellites and their orbit’s predictability are used in satellite navigation systems, such as GPS. Space probes are satellites designed for robotic space exploration outside of Earth, and space stations are in essence crewed satellites. There are lots of other usages of satellite,s for example, experimental satellites(Biosatellites) are satellites designed to carry living organisms, generally for scientific experimentation; Weapon satellites for Space weapons or Anti-satellite weapons.

Issues like space debris, radio and light pollution are increasing in magnitude and at the same time lack progress in national or international regulation.
Experimental Sketch:

Data Source:
https://www.destinationspace.uk/how-we-use-satellites/how-far-away-close-are-satellites/