These notes are a brief outline of the various bodies that govern the internet. Keep in mind the internet isn’t a clearly defined body, so governing it isn’t like governing a state. Rather, these bodies create standards that the companies who run internet businesses can implement.
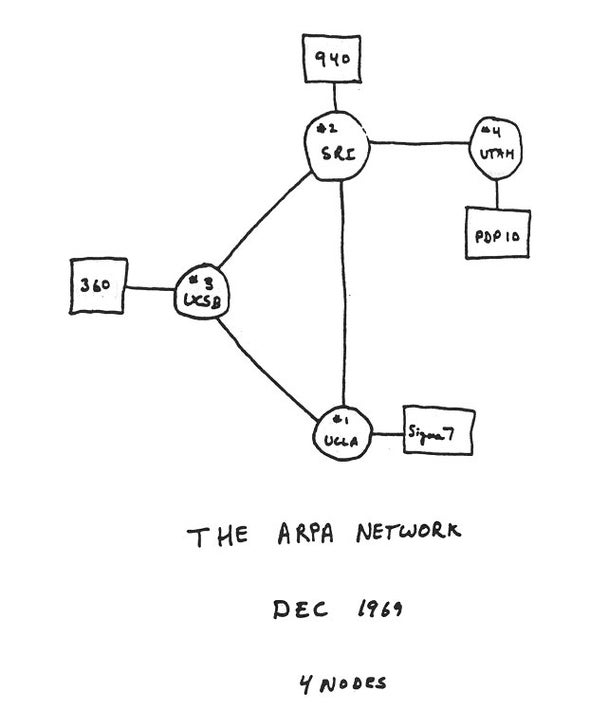
The internet grew out of the ARPAnet, originally set up in 1969, consisting of four nodes: Stanford Research Institute, UCLA, UCSB, and the University of Utah. Here’s the original map:
The core process of internet governance is the Request for Comment (RFC) document. When you want to set a new standard, you write an RFC document and ask for comments. Then a bunch of people argue about it, re-write it, argue some more, re-write some more, until consensus emerges. The bodies described below all exist to manage the process in some way or another.
Internet Society (ISOC)
- A not-for-profit organization, based in Washington DC.
- Funded by membership fees. Anyone can become a member.
- Contains IETF, IAB, IESG, IRTF, IRSG, RFC Editor
- The ISOC maintains a useful chart of the Internet ecosystem
Internet Activities Board (IAB)
- Originally a DARPA advisory board
- Nominated by the IETF
- Considers the overall architecture of internet standards, at a more general level than IETF working groups.
Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF)
- Reports to ISOC
- Is an open body – has no formal membership
- Funded by meeting fees
- Most of the communication is through mailing lists
- Is a collection of working groups which develop standards for various internet protocols and best practices
Internet Engineering Steering Group (IESG)
- Reports to ISOC
- Made up of the area directors of IETF, nominated by the nominating committee (see RFC 2727) of the IETF
- Vets and approves IETF standards that are ratified by ISOC
Internet Research Task Force (IRTF)
- Parallel to the IETF, this group works on long-term internet standards research
- Chair is appointed by the IAB
- The IRTF has research groups that parallel the IETF’s working groups.
Internet Research Steering Group (IRSG)
- Parallels the IESG
- Reports to ISOC
- Made up of the area directors of IRSG, nominated by the nominating committee
- Reviews and approves IRTF documents
- Maintains the RFCs
- Originally one guy. First Steve Crocker, then for a long time, Jon Postel. Crocker wrote RFC 1, the first RFC.
- Currently handled by Association Management Solutions, Inc.
- RFC 2026 details the RFC process.
Internet Corporation for Assigned Nam es and Numbers (ICANN)
- Sets the policies for the assignment of internet names and numbers.
- Not-for-profit, based in California
- Has no regular members, but an invited board of 16 members
- Has a government advisory committee made up of advisors from 111 countries.
- Funded by domain name registry sales
- Its executive branch is IANA.
- ICANN’s Beginner’s Guides are helpful introductions to participating in ICANN, to IP addresses, and more.
Internet Assigned Names Authority (IANA)
- ICANN’s Executive branch
- The IANA Functions Explained in 180 seconds
- This video covers the IANA Stewardship Processes, i.e. how accountability is maintained within ICANN and IANA
- Made up of five Regional Internet Registries (RIRs):
- AFRINIC (Africa Region)
- APNIC (Asia/Pacific Region)
- ARIN (North America Region)
- LACNIC (Latin America and some Caribbean Islands)
- RIPE NCC (Europe, the Middle East, and Central Asia)
- Besides the Domain Name System, IANA also maintains the list of Autonomous System Numbers (ASNs). Autonomous Systems are aggregates of IP addresses run by a single provider.
- Contracts Verisign to maintain the root Domain Name System
- Root DNS is a network of 13 redundant root servers
- Root servers maintain the root zone files, which are the core DNS description files. All DNS servers eventually contribute to the updating of these files.